VMware services
What is vmware VPXD?
VPXD-It is Vcenter Server Service. If this service is stopped then we will not able to connect to Vcenter Server via Vsphere client. VPXA-It is the agent of Vcenter server. also known as mini vcenter server which is installed on the each esx server which is managed by Vcenter server
What is VPXA?
The vCenter Server Agent, also referred to as vpxa or the vmware-vpxa service, is what allows a vCenter Server to connect to a ESX host. Specifically, vpxa is the communication conduit to the hostd, which in turn communicates to the ESX kernel
What is vCSA?
VMware vCenter Server Virtual Appliance (vCSA) features and benefits. ... It provides exactly the same functionality as the traditional Windows vCenter Server but packaged in a Linux distribution
What is Vpostgres database?
VMware vSphere Update Manager can't use the embedded vPostgres database! For VMware vSphere Update Manager you need a Microsoft SQL (Express)database. When combining the vCenter Server, PSC and VUM on one server, two different databases engines are used
How do I reset Vcenter appliance?
Log in to the vSphere Web Client with a vCenter Single Sign-on administrator account. Navigate to Administration > Deployment > System Configuration. Click Nodes, select the vCenter Server Appliance node and click the Related Objects tab. Right-click on the service you want to restart and select Restart.
How does Vcenter communicate with each ESXI server?
vSphere Client can communicate with both a vCenter Server instance and anESXi host. Access to the ESXi host is provided by a vCenter Server agent named vpxa. The vpxa process is started on the ESXi host when it is added to the vCenter Server inventory. vpxa communicates with the ESXi host agent named hostd
HOSTD:- It is the process that authenticates users and keeps track of which users and groups have which privileges. It also allows you to create and manage local users. The HOSTD process provides a programmatic interface to VMkernel and is used by direct VI Client connections as well as the VI API.
What is the difference between VPXA, VPXD, HOSTD?
Hostd is demon or service runs in every ESXi host and performs major tasks like, VM power on, local user management etc. But when ESXi host joins in a vCenter server Vpxa agent gets activated and talk to Vpxd service which runs in vCenter server. So the conclusion is Vpxd talks to Vpxa and Vpxa talks to hostd, this is how Vpxd (vCenter demon) talks to hostd demon via Vpxa agents.
What is the difference between ESXI and ESX?
It's been a long debate that everyone has been asked by what is the difference between ESX and ESXi. ... ESX (Elastic Sky X) is the VMware's enterprise server virtualization platform. In ESX, VMkernel is the virtualization kernel which is managed by a console operating system which is also called as Service console
What initial tasks can be done by DCUI-
• Set administrative password
• Configure networking
• Perform simple network tests
• View logs
• Restart agents
• Restore defaults
Describe VMware System Image Design-
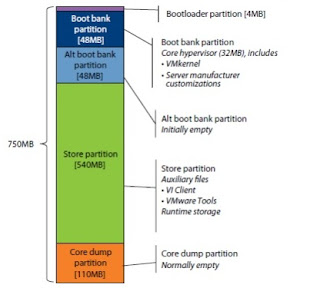
The ESXi system has two independent banks of memory, each of which stores a full system image, as a fail-safe for applying updates. When you upgrade the system, the new version is loaded into the inactive bank of memory, and the system is set to use the updated bank when it reboots. If any problem is detected during the boot process, the system automatically boots from the previously used bank of memory. You can also intervene manually at boot time to choose which image to use for that boot, so you can back out of an update if necessary.
At any given time, there are typically two versions of VI Client and two versions of VMware Tools in the store partition.
What is vnic, vmnic and vmk.
Vmware default policy.
:STN
1:Security.
Promoscuous mode
Mac address changes .
Frogged transmit.
2: Traffic shaping
Average bandwidth.
Peak bandwidth.
Burst size.
3:Teaming failover and loadbalancing
1.Load balancing
2.Network failer detection.
3.Notify switches.
4.Failback.
5.Active adaptors.



No comments:
Post a Comment